Deepesh Joseph
August 2006
Information Management (IM) refers to any activity that leads to effective collection, storage, retrieval and analysis of information by focusing on business strategy and by continuously improving business competitiveness and adaptability. The ultimate goal of any IM job is to add up to the combined efforts to meet the required business strategy. The business strategy can be, say, “making Government more approachable and transparent to the citizens”. To meet this goal, the Federal Government has to implement scalable Information Management solutions that will make strategic use of IT as an enabling medium. This is a typical situation where we require professional IM expertise and skills. Depending upon the nature of business and the complexity of the IM project, there exists various professional fields of expertise within the IM field. IM field is very diverse and its hard to cover all the skill positions. A typical map and guide to IM field is depicted in Figure (a).
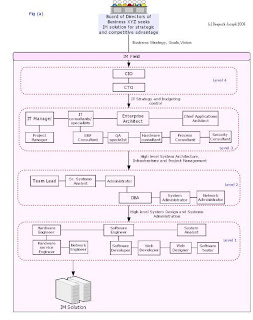
Figure (a) shows a typical IM field where in a business strategy gets converted to IM solution. As shown in the figure, there are 4 major levels of skills cloud. All the skills sets works in a synergistic manner towards the common business goal. I shall briefly state each of the skill position.
Level 4: Level 4 is the Chief Officers' level where the business strategy is mapped to IT strategy and architecture. On the top, we have
4.1 CIO or Chief Information Officer who is responsible for providing technology vision and leadership to conceive, build and implement multiple IT projects on time and within budget. CIO should have technology skills as well as business skills to effectively understand the business vision and then utilize IT wisely and cost effectively to realize the vision. So CIO is a strategist as well as a technologist.
4.2 CTO or Chief Technology Officer is more technology oriented job which requires knowledge about existing and emerging technologies and thus advice on technology adoption. CTO should be capable of creating an organizational vision for new technologies and oversee and manage the firm's technological operations and infrastructure.
Level 3: Level 3 consists of the IT managers, Architects and Specialists who work on building the feasible architectures, specifications project management methodologies.
3.1 IT Manager is responsible for managing individuals involved in the activities of developing, designing, debugging, installing, modifying, testing, analyzing or maintaining applications programs and other IT systems. IT manager ensures effective coordination and technical support between programmers, developers, testers, interfacing system groups, and end-users and adherence to quality standards. The position requires extensive experience in managing IT projects and systems.
3.1.1 Project Manager applies or ensures the application of a standard, defined methodology to the project, and provides the leadership skills necessary to control the execution of the project tasks, as defined in the methodology.
3.2 IT consultants/specialists are either outsourced or in house manpower who have specialized skills in various aspects of system architecture development and business process improvement. Well known IT consultant job titles are -
3.2.1 ERP consultant
3.2.2 Business Process consultant
3.2.3 Security Consultant
3.2.4QA specialist
3.2.5 Hardware specialist
3.3 Enterprise Architect is a strategic person who is passionate about delivering business orientated IT outcomes by adopting an architectural approach. This position requires ability to articulate strategies, ideas, positions and recommendations in written, visual and verbal forms such as Enterprise Architect frameworks, UML/Object Oriented Design and Architecture Tools.
3.4 Chief Applications Architect is a highly skilled position whose major responsibilities includes developing and implementing standards and procedures for data, data modeling, data architecture and software applications. This position plans, analyzes, and develops requirements for application development and enhancement of all critical applications.
Level 2: Level 2 consists of the Team leads and administrators who actually does hands-on on various senior System development and Administration jobs such as follows.
2.1 Team Leader usually is the senior member of a software development team who performs high level system/db designs, software testing and some amount of Quality Assurance. He should have excellent communication skills and team management skills.
2.2 Sr. Systems Analyst acts as a liaison between business people who have a business problem and technology people who know how to create solutions. In doing so he manages the organization's documentation of business requirements, including use cases and other system analysis docs to ensure that the project team develops solutions that meet the business goal .
2.3 Administrators manages and maintains specific areas of IT infrastructure such as servers and other hardware, Database and Network. Well known job titles are System Administrator, DBA and Network Admin.
Level 1: Level 1 consists of the Engineering and Analyst team that perform the basic day to day System Development tasks. At this level all the the business strategy is in the form of clear system specifications such as DFDs, ERDs, System flows, Program logic flows and detailed hardware/network configurations. The job in this level requires knowledge of basic Software Engineering methodologies, Hardware/Network technologies, configurations and troubleshooting. Its essential to have skills in System Analysis and design techniques, Programming, Software testing and hardware/network configuration and maintenance. Well known job titles are as follows.
1.1 Hardware Engineer is responsible for configuring, troubleshooting and servicing hardware/network. Well known job titles are -
1.1.1 Hardware service Engineer
1.1.2 Network Engineer
1.2 Software Engineer is responsible for developing software based on the system specifications and acceptable programming techniques and standards so that the developed IM solution will satisfy the business goal. Major job titles are -
1.2.1 Software Engineer/Developer
1.2.2 Web Developer
1.2.3 Web designer
1.2.4 Software Tester
August 2006
Information Management (IM) refers to any activity that leads to effective collection, storage, retrieval and analysis of information by focusing on business strategy and by continuously improving business competitiveness and adaptability. The ultimate goal of any IM job is to add up to the combined efforts to meet the required business strategy. The business strategy can be, say, “making Government more approachable and transparent to the citizens”. To meet this goal, the Federal Government has to implement scalable Information Management solutions that will make strategic use of IT as an enabling medium. This is a typical situation where we require professional IM expertise and skills. Depending upon the nature of business and the complexity of the IM project, there exists various professional fields of expertise within the IM field. IM field is very diverse and its hard to cover all the skill positions. A typical map and guide to IM field is depicted in Figure (a).

Figure (a) shows a typical IM field where in a business strategy gets converted to IM solution. As shown in the figure, there are 4 major levels of skills cloud. All the skills sets works in a synergistic manner towards the common business goal. I shall briefly state each of the skill position.
Level 4: Level 4 is the Chief Officers' level where the business strategy is mapped to IT strategy and architecture. On the top, we have
4.1 CIO or Chief Information Officer who is responsible for providing technology vision and leadership to conceive, build and implement multiple IT projects on time and within budget. CIO should have technology skills as well as business skills to effectively understand the business vision and then utilize IT wisely and cost effectively to realize the vision. So CIO is a strategist as well as a technologist.
4.2 CTO or Chief Technology Officer is more technology oriented job which requires knowledge about existing and emerging technologies and thus advice on technology adoption. CTO should be capable of creating an organizational vision for new technologies and oversee and manage the firm's technological operations and infrastructure.
Level 3: Level 3 consists of the IT managers, Architects and Specialists who work on building the feasible architectures, specifications project management methodologies.
3.1 IT Manager is responsible for managing individuals involved in the activities of developing, designing, debugging, installing, modifying, testing, analyzing or maintaining applications programs and other IT systems. IT manager ensures effective coordination and technical support between programmers, developers, testers, interfacing system groups, and end-users and adherence to quality standards. The position requires extensive experience in managing IT projects and systems.
3.1.1 Project Manager applies or ensures the application of a standard, defined methodology to the project, and provides the leadership skills necessary to control the execution of the project tasks, as defined in the methodology.
3.2 IT consultants/specialists are either outsourced or in house manpower who have specialized skills in various aspects of system architecture development and business process improvement. Well known IT consultant job titles are -
3.2.1 ERP consultant
3.2.2 Business Process consultant
3.2.3 Security Consultant
3.2.4QA specialist
3.2.5 Hardware specialist
3.3 Enterprise Architect is a strategic person who is passionate about delivering business orientated IT outcomes by adopting an architectural approach. This position requires ability to articulate strategies, ideas, positions and recommendations in written, visual and verbal forms such as Enterprise Architect frameworks, UML/Object Oriented Design and Architecture Tools.
3.4 Chief Applications Architect is a highly skilled position whose major responsibilities includes developing and implementing standards and procedures for data, data modeling, data architecture and software applications. This position plans, analyzes, and develops requirements for application development and enhancement of all critical applications.
Level 2: Level 2 consists of the Team leads and administrators who actually does hands-on on various senior System development and Administration jobs such as follows.
2.1 Team Leader usually is the senior member of a software development team who performs high level system/db designs, software testing and some amount of Quality Assurance. He should have excellent communication skills and team management skills.
2.2 Sr. Systems Analyst acts as a liaison between business people who have a business problem and technology people who know how to create solutions. In doing so he manages the organization's documentation of business requirements, including use cases and other system analysis docs to ensure that the project team develops solutions that meet the business goal .
2.3 Administrators manages and maintains specific areas of IT infrastructure such as servers and other hardware, Database and Network. Well known job titles are System Administrator, DBA and Network Admin.
Level 1: Level 1 consists of the Engineering and Analyst team that perform the basic day to day System Development tasks. At this level all the the business strategy is in the form of clear system specifications such as DFDs, ERDs, System flows, Program logic flows and detailed hardware/network configurations. The job in this level requires knowledge of basic Software Engineering methodologies, Hardware/Network technologies, configurations and troubleshooting. Its essential to have skills in System Analysis and design techniques, Programming, Software testing and hardware/network configuration and maintenance. Well known job titles are as follows.
1.1 Hardware Engineer is responsible for configuring, troubleshooting and servicing hardware/network. Well known job titles are -
1.1.1 Hardware service Engineer
1.1.2 Network Engineer
1.2 Software Engineer is responsible for developing software based on the system specifications and acceptable programming techniques and standards so that the developed IM solution will satisfy the business goal. Major job titles are -
1.2.1 Software Engineer/Developer
1.2.2 Web Developer
1.2.3 Web designer
1.2.4 Software Tester